Cataract surgery is a common procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by cataracts, which cloud the eye’s natural lens, leading to blurred vision and other complications.
Turkey has emerged as a prominent destination for medical tourism, especially for eye surgeries, owing to its affordable healthcare system, advanced technology, and experienced surgeons.

What is a Cataract Surgery?
Cataract surgery is a medical procedure aimed at removing the cloudy lens of the eye caused by cataracts, a condition characterized by the gradual opacification of the lens, leading to impaired vision.
This surgery restores clear vision by replacing the cloudy lens with a transparent artificial lens known as an intraocular lens (IOL).
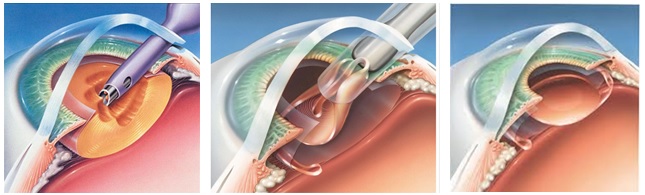
Overview of Cataracts
Cataracts develop when proteins in the lens of the eye clump together, forming a cloudy area. They are a common age-related condition, though they can also result from trauma, certain medications, or underlying health issues such as diabetes. Symptoms typically include:
- Blurred or cloudy vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Double vision
- Fading or yellowing of colors
Cataracts can progress over time, ultimately leading to significant vision loss if left untreated. Cataract surgery is often the most effective treatment to restore vision.
Benefits of Cataract Surgery
- Improved Vision: The primary benefit of cataract surgery is the significant improvement in vision. Most patients experience clearer vision after the cloudy lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Many can achieve 20/25 vision or better, often without needing glasses.
- Increased Quality of Life: Enhanced vision can greatly improve daily activities, such as reading, driving, and engaging in hobbies. Many patients report a significant boost in their overall quality of life post-surgery.
- Quick Recovery: Cataract surgery is typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home shortly after the procedure. Most patients experience a rapid recovery, with many noticing improved vision within a few days.
- High Success Rate: Cataract surgery has a success rate of over 95%, meaning that the vast majority of patients achieve their desired vision outcomes.
- Reduced Risk of Falls and Injuries: Improved vision reduces the risk of falls and related injuries, which can be particularly important for elderly patients.
- Customization with IOLs: Advances in technology allow patients to choose from various types of intraocular lenses, such as multifocal or toric lenses, tailored to their specific vision needs and lifestyle.
- Minimal Pain: Most patients report minimal discomfort during and after the procedure due to the use of local anesthesia and sedation.
- Long-Lasting Results: The results of cataract surgery are long-lasting. Most patients do not need additional surgery, and the artificial lens can last a lifetime.
Risks of Cataract Surgery
- Infection: Although rare, there is a risk of infection following surgery, which can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
- Intraoperative Complications: Complications can occur during surgery, such as damage to the cornea or retina, which may impact the outcome.
- Inflammation: Some patients may experience inflammation within the eye after surgery, leading to discomfort and potentially affecting vision.
- Retinal Detachment: Although rare, cataract surgery can increase the risk of retinal detachment, which may require additional surgical intervention.
- Glaucoma: There is a slight risk of developing glaucoma following cataract surgery due to changes in eye pressure.
- Visual Disturbances: Patients may experience glare, halos, or double vision after surgery, particularly with certain types of IOLs. These symptoms may diminish over time but can persist in some cases.
- Need for Glasses: While many patients achieve excellent vision after surgery, some may still require glasses for reading or other activities, especially if a monofocal lens is used.
Capsular Opacification: In some cases, the thin membrane that holds the IOL in place (the capsule) can become cloudy over time, leading to vision problems. This condition, known as secondary cataract, can be treated with a simple outpatient laser procedure
QUICK, 100% FREE ONLINE QUOTE
Factors that influence the price of the Cataract procedure in Turkey.
Type of Intraocular Lens (IOL)
One of the most significant factors affecting the price of cataract surgery is the type of intraocular lens (IOL) chosen for the procedure.
IOLs are artificial lenses implanted in the eye to replace the cloudy natural lens affected by cataracts. The choice of IOL can lead to considerable differences in costs, particularly given the various available options.
- Monofocal IOLs: These lenses provide clear vision at one distance—either near or far—but not both. They are usually the least expensive option and are often covered by basic insurance plans.
- Multifocal IOLs: Designed to offer multiple focal points, these lenses allow patients to see clearly at various distances without the need for glasses. However, they come at a premium price and may not be covered by all insurance plans.
- Toric IOLs: Specifically designed for patients with astigmatism, toric lenses can help improve vision quality. Their specialized nature typically results in higher costs compared to standard monofocal lenses.
- Premium IOLs: These advanced lenses incorporate cutting-edge technology, offering features such as accommodating or extended depth of focus. While they provide superior vision quality and functionality, they also carry a significantly higher price tag.
Surgeon’s Experience and Credentials
The surgeon’s qualifications, experience, and reputation can substantially influence the cost of cataract surgery.
Highly skilled ophthalmologists, particularly those with specialized training and a successful track record in cataract procedures, often charge higher fees.
- Training and Certification: Surgeons who have completed fellowship training or have additional certifications may charge more due to their specialized skills and expertise.
- Success Rate: A surgeon’s history of successful outcomes can justify higher costs. Patients may be willing to pay more for a surgeon with a proven track record of minimal complications and satisfied patients.
- Patient Reviews: Researching online reviews and testimonials can provide insights into a surgeon’s quality of care and help justify the cost of selecting a particular practitioner.
Facility Quality and Type
The type of facility where the surgery is performed can have a considerable impact on pricing. Patients can choose from a variety of settings, including:
- Private Clinics: These establishments often provide a higher level of personalized care, advanced technology, and comfort but may charge more for their services compared to public hospitals.
- Public Hospitals: While generally less expensive, public facilities may have longer waiting times and potentially lower levels of individualized care.
- Ambulatory Surgery Centers: These specialized facilities focus solely on outpatient procedures and may offer competitive pricing. Their efficiency can help keep costs down, but the quality of care can vary widely, making it essential for patients to research these centers thoroughly.
Location of the Facility
The geographical location of the surgery center is another crucial factor in determining the cost of cataract surgery.
Prices can vary significantly between urban and rural areas, as well as between different cities in Turkey.
- Major Cities vs. Smaller Towns: Facilities in major cities like Istanbul or Ankara often have higher operational costs, which can lead to more expensive pricing compared to smaller towns like Izmir or Antalya. However, larger cities may also offer more advanced technology and a wider selection of experienced surgeons.
- Local Economic Factors: The cost of living in a specific region can influence healthcare pricing. Areas with a higher cost of living may see increased medical fees as facilities adjust their prices to match local economic conditions.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Preoperative assessments and postoperative care are critical components of the cataract surgery process and can significantly influence the overall cost.
- Initial Consultation: Before surgery, patients typically undergo a comprehensive eye examination that includes various tests to assess their vision and determine the best IOL for their needs. The costs associated with these assessments can vary.
- Diagnostic Tests: Additional tests may be necessary to evaluate the patient’s eye health, such as corneal topography, retinal examinations, and measurements for the IOL. The complexity and number of these tests can contribute to the total price.
- Follow-Up Visits: Postoperative care is essential for monitoring recovery and ensuring optimal outcomes. The frequency and type of follow-up visits required can impact overall costs. Patients may need several follow-up appointments to monitor healing and vision stability, particularly if complications arise.
Anesthesia Type
While cataract surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, the method of anesthesia can also influence the overall price.
- Local Anesthesia: Most patients receive local anesthesia, which is less expensive compared to general anesthesia. This method minimizes costs while still providing adequate pain management during the procedure.
- Sedation Options: Some patients may require additional sedation for comfort, which can increase the cost. The type of sedation used and the need for an anesthesiologist can affect the total fee for the procedure.
Health Insurance Coverage
Understanding health insurance coverage is essential when considering the price of cataract surgery.
- Insurance Benefits: Many insurance plans cover basic cataract surgery; however, patients may have to pay extra for advanced IOLs or premium surgical techniques. It is crucial to review policy details to determine what is covered.
- Out-of-Pocket Costs: Patients should consider potential out-of-pocket expenses, including deductibles, copays, and any costs associated with services not covered by insurance.
- Pre-Approval Requirements: Some insurance providers may require pre-approval for certain procedures or IOLs, which can affect scheduling and final costs.
Technological Advancements
The use of advanced technology in cataract surgery can lead to increased costs.
- Laser-Assisted Surgery: Patients opting for laser-assisted cataract surgery may incur higher fees due to the sophisticated equipment and technology used. This method can offer benefits like greater precision and less discomfort, making it appealing despite the higher price.
- Innovative Diagnostic Equipment: Advanced diagnostic tools used in preoperative assessments, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or high-resolution imaging, can contribute to the overall cost of surgery.
Patient Health and Medical History
A patient’s overall health and any existing medical conditions can influence the pricing of cataract surgery.
- Additional Health Considerations: Patients with comorbidities, such as diabetes or hypertension, may require further evaluations and monitoring, leading to additional costs. These evaluations ensure the patient is fit for surgery and minimize potential risks.
- Complex Cases: Patients with previous eye surgeries, significant astigmatism, or other eye conditions may necessitate more complex surgical techniques, which can elevate costs.
Length of Hospital Stay
While most cataract surgeries are performed on an outpatient basis, some patients may require overnight hospitalization, particularly if complications arise.
- Facility Charges: The costs associated with an extended hospital stay can add significantly to the total price of surgery. This includes room charges, nursing care, and any additional treatments needed during the stay.
Packages and Promotions
Many clinics and hospitals in Turkey offer promotional packages that can influence the final cost of cataract surgery.
- All-Inclusive Packages: Some facilities provide all-inclusive packages that encompass consultations, surgery, postoperative care, and follow-up visits. These packages may offer cost savings compared to paying for each service individually.
- Seasonal Promotions: Patients may find seasonal discounts or promotional offers that can help lower the overall expense of cataract surgery, making it worthwhile to shop around for the best deals.
Currency Exchange Rates
For international patients considering cataract surgery in Turkey, currency exchange rates can play a crucial role in determining the final cost of the procedure.
- Fluctuating Rates: The value of the Turkish Lira against other currencies can fluctuate, affecting the total price. Patients should monitor exchange rates and consider timing their surgery accordingly to take advantage of favorable rates.
Reputation and Accreditation of the Facility
The reputation and accreditation of the healthcare facility can also influence the price of cataract surgery.
- Accredited Facilities: Hospitals and clinics accredited by reputable organizations often adhere to higher standards of care and may charge more due to their enhanced service offerings and quality assurance measures.
- Patient Outcomes: Facilities known for their high success rates and positive patient outcomes may command higher prices due to the trust they have built within the community.
Additional Services and Amenities
The overall experience of patients during their cataract surgery can vary based on the services and amenities offered by the facility.
- Comfort and Convenience: Some clinics provide additional amenities such as private rooms, concierge services, and transportation assistance, which can increase costs but enhance the overall patient experience.
- Personalized Care: Facilities that offer more personalized attention and comprehensive care may charge higher fees due to the increased resources and staff required to maintain such a level of service.
Prices of all types of the Cataract operation in Turkey.
Phacoemulsification
Definition and Details
Phacoemulsification is the gold standard for cataract surgery, representing a major advancement in the field of ophthalmology. This procedure involves the use of ultrasonic energy to break up the cloudy lens into smaller fragments, making removal easier and less traumatic for the eye.
During the surgery, the surgeon makes a small incision (typically between 2.2 mm to 2.8 mm) in the cornea.
This smaller incision allows for a quicker recovery and reduces the risk of complications compared to larger incisions. The surgeon inserts a phacoemulsification probe, which emits ultrasound waves that emulsify the cataract lens into a viscous liquid, allowing it to be suctioned out easily.
Once the cloudy lens is removed, an intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted to replace the natural lens. The IOL can be monofocal, multifocal, or toric, depending on the patient’s visual needs.
Phacoemulsification is usually performed under local anesthesia and can be completed in less than 30 minutes, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in vision shortly after surgery.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Assessment: The ophthalmologist conducts a thorough examination of the eye, measuring the size and shape of the eye to determine the appropriate IOL.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is applied to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- Incision Creation: A small incision is made at the edge of the cornea.
- Capsulorhexis: A circular opening is made in the anterior capsule of the lens to access the cataract.
- Phacoemulsification: The ultrasound probe is inserted, and ultrasonic waves break the cataract into tiny fragments.
- Aspirating the Lens: The broken pieces are gently suctioned out of the eye using an irrigation/aspiration device.
- IOL Implantation: The selected intraocular lens is inserted through the incision and positioned in the capsular bag.
- Closure: The incision is self-sealing, requiring no stitches in most cases.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive instructions for eye care and schedule follow-up appointments.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Ultrasound Biometry: $50 – $150
- Phacoemulsification Surgery: $1,500 – $3,000
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $2,050 – $4,850
Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE)
Definition and Details
Extracapsular cataract extraction is a traditional surgical method that allows for the removal of the entire cataract lens, including its capsule, through a larger incision (approximately 10-12 mm). This technique may be particularly beneficial for patients with more advanced cataracts or when the cataract is too dense for phacoemulsification.
During ECCE, the surgeon makes a larger incision in the eye, which provides direct access to the cataract.
The cloudy lens is removed in one piece, which may reduce the risk of lens fragments remaining in the eye.
After the cataract is extracted, an IOL is implanted. The larger incision may require sutures, leading to a slightly longer recovery time compared to phacoemulsification.
ECCE is usually performed under local anesthesia, and while it is effective, it has become less common due to the rise of phacoemulsification, which offers faster recovery and reduced risk of complications.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Examination: The patient undergoes an eye examination to determine the appropriate surgical approach and lens type.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the eye and minimize discomfort.
- Incision Creation: A larger incision is made on the edge of the cornea.
- Capsulotomy: The surgeon creates an opening in the anterior capsule of the lens to access the cataract.
- Cataract Removal: The entire cataract lens is gently extracted through the incision.
- IOL Insertion: An intraocular lens is placed into the eye to replace the natural lens.
- Closure: The incision is closed, often requiring stitches.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive instructions on how to care for their eyes post-surgery.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- ECCE Surgery: $1,200 – $2,500
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $1,700 – $4,050
Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery
Definition and Details
Laser-assisted cataract surgery incorporates advanced technology using a femtosecond laser to enhance precision during the cataract removal process.
The laser is utilized for several steps of the procedure, including creating the corneal incision, capsulotomy (the opening in the lens capsule), and breaking up the cataract lens.
This method offers several advantages, including increased accuracy in incision placement, improved safety by reducing the risk of complications, and the potential for a quicker recovery.
The laser’s precision minimizes the energy required to break up the cataract, which may result in less swelling and discomfort postoperatively.
Laser-assisted cataract surgery is performed under local anesthesia and usually takes less time than traditional methods, with many patients experiencing excellent visual outcomes shortly after the procedure.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Assessment: A thorough evaluation of the eye, including imaging studies to guide the laser procedure.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is provided to ensure comfort during surgery.
- Laser Incision Creation: The femtosecond laser creates precise incisions in the cornea.
- Capsulotomy with Laser: The laser is used to create an accurate opening in the lens capsule.
- Cataract Fragmentation: The laser softens the cataract, allowing for easier removal.
- Aspirating the Lens: The fragmented lens is suctioned out of the eye.
- IOL Implantation: An intraocular lens is placed in the eye.
- Closure: The incisions are self-sealing, requiring no stitches in most cases.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive specific aftercare instructions and schedule follow-ups.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Laser-Assisted Surgery: $2,000 – $4,000
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $2,500 – $5,550
Small Incision Cataract Surgery (SICS)
Definition and Details
Small incision cataract surgery (SICS) is a surgical technique that uses a slightly larger incision than phacoemulsification but is still considered minimally invasive. The procedure is often employed in situations where phacoemulsification may not be possible, such as in certain medical conditions or in rural areas with limited resources.
During SICS, the surgeon creates a small incision (about 6 mm) in the cornea. The cloudy lens is then manually extracted from the eye.
Although this technique requires more manual manipulation than phacoemulsification, it is effective in removing cataracts and allows for the implantation of an intraocular lens afterward.
SICS is a preferred option in some developing countries due to its lower cost and fewer equipment requirements, making it accessible for more patients.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Evaluation: The patient undergoes a comprehensive eye examination to determine candidacy for SICS.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is comfortable.
- Incision Creation: A small incision is made in the cornea.
- Capsulorhexis: The surgeon creates an opening in the anterior capsule of the lens.
- Cataract Removal: The lens is extracted through the small incision using specialized instruments.
- IOL Insertion: An artificial lens is placed in the eye.
- Closure: The incision may be self-sealing and usually does not require stitches.
- Postoperative Care: Patients are given instructions for aftercare and schedule follow-up visits.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- SICS Surgery: $1,000 – $2,500
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $1,500 – $4,050
Manual Cataract Surgery
Definition and Details
Manual cataract surgery is a technique that involves the traditional, hands-on approach to cataract removal without the assistance of advanced technology like lasers.
This method is typically employed when patients have specific conditions that may complicate other surgical methods or when advanced equipment is unavailable.
In manual cataract surgery, the surgeon creates an incision, removes the cloudy lens, and then implants an intraocular lens.
While this method may have a longer recovery period and slightly higher risks of complications compared to more modern techniques, it can still yield successful outcomes for many patients.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the eye to determine the best surgical approach.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to ensure patient comfort.
- Incision Creation: A corneal incision is made, typically larger than those used in phacoemulsification.
- Capsulotomy: An opening is created in the anterior capsule of the lens to access the cataract.
- Cataract Removal: The surgeon manually removes the cloudy lens using specialized instruments.
- IOL Insertion: An artificial lens is placed in the eye.
- Closure: The incision is closed, often requiring stitches.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive detailed care instructions and follow-up appointments.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Manual Surgery: $800 – $2,000
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $1,300 – $3,550
Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery
Definition and Details
Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery is an advanced, precision technique that uses a femtosecond laser to perform several critical steps of the procedure.
This includes creating corneal incisions, performing capsulotomy, and fragmenting the cataract lens. The use of laser technology enhances the accuracy and safety of the surgery.
The laser’s ability to create highly precise incisions reduces the risk of complications and improves the overall safety profile of cataract surgery.
Patients often experience less swelling and a quicker recovery due to the minimally invasive nature of the procedure. This technique has become increasingly popular among patients seeking the latest advancements in eye care.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Evaluation: A detailed examination to plan the surgery and select the appropriate IOL.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is provided to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Laser Incision Creation: The femtosecond laser creates precise incisions in the cornea.
- Laser Capsulotomy: The laser performs an accurate opening in the lens capsule.
- Cataract Fragmentation with Laser: The cataract is fragmented into smaller pieces using the laser, facilitating easier removal.
- Lens Aspiration: The fragmented lens material is suctioned out of the eye.
- IOL Implantation: An intraocular lens is inserted into the eye.
- Closure: The incisions are typically self-sealing.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive aftercare instructions and schedule follow-ups.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Femtosecond Laser Surgery: $2,500 – $5,000
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $3,000 – $6,550
Scleral Fixated Intraocular Lens Surgery
Definition and Details
Scleral fixated intraocular lens surgery is a specialized technique used when there is insufficient capsular support for the placement of a standard intraocular lens. This situation can occur in patients who have experienced trauma, previous surgeries, or conditions that have weakened the lens capsule.
In this procedure, the surgeon uses sutures to anchor the IOL to the sclera (the white part of the eye) instead of placing it directly in the capsule. This method ensures the stability of the lens, allowing for improved visual outcomes.
Scleral fixation may require a more extended surgical time and may involve additional complexities due to the lack of capsular support.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Assessment: Detailed eye examination to assess the condition of the lens capsule and determine the need for scleral fixation.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is provided to minimize discomfort.
- Incision Creation: The surgeon creates an incision in the cornea.
- Capsulotomy: An opening is made in the lens capsule if possible.
- IOL Preparation: The intraocular lens is prepared for scleral fixation.
- Scleral Suturing: Sutures are passed through the sclera to anchor the IOL securely.
- Lens Positioning: The IOL is positioned within the eye.
- Closure: The incision is closed, often requiring sutures.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive specific care instructions and schedule follow-ups.
Cost Breakdown
Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
Scleral Fixation Surgery: $1,500 – $3,500
Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
Total Estimated Cost: $2,000 – $5,050
Cataract Surgery with Toric IOL Implantation
Definition and Details
Cataract surgery with toric intraocular lens (IOL) implantation is designed for patients who have both cataracts and pre-existing astigmatism. Astigmatism is caused by an irregular curvature of the cornea, leading to blurred or distorted vision. Toric IOLs are specially designed to correct astigmatism during cataract surgery.
This procedure typically follows a similar path to traditional cataract surgery but includes the insertion of a toric lens, which has specific alignment requirements.
The surgeon must carefully position the lens to ensure optimal visual correction. Patients can often achieve clearer vision without the need for glasses or contact lenses post-surgery.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Assessment: Comprehensive eye evaluation to measure astigmatism and determine the best IOL type.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is administered for patient comfort.
- Incision Creation: A small incision is made in the cornea.
- Capsulotomy: An opening is created in the lens capsule.
- Cataract Removal: The cloudy lens is broken up and suctioned out.
- Toric IOL Insertion: The toric lens is carefully positioned in the eye, ensuring proper alignment.
- Closure: The incision is typically self-sealing.
- Postoperative Care: Patients are given specific instructions for care and follow-up visits.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Toric IOL Surgery: $2,000 – $4,000
- Toric IOL Implantation: $600 – $1,500
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $2,900 – $6,050
Multifocal IOL Implantation Surgery
Definition and Details
Multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) implantation surgery is a specialized type of cataract surgery aimed at providing patients with a broader range of vision.
Multifocal IOLs contain multiple focal points, allowing patients to see clearly at different distances near, intermediate, and far without the need for glasses.
This procedure involves the standard steps of cataract surgery, with the added complexity of selecting and positioning the multifocal IOL.
Patients often appreciate the ability to function without glasses in their daily activities, significantly improving their quality of life. However, multifocal lenses may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with specific visual needs or conditions.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Evaluation: Comprehensive assessment to determine the appropriateness of multifocal IOLs.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is provided for comfort.
- Incision Creation: A small incision is made in the cornea.
- Capsulotomy: The lens capsule is opened to access the cataract.
- Cataract Removal: The cloudy lens is emulsified and aspirated.
- Multifocal IOL Insertion: The multifocal lens is inserted and positioned within the eye.
- Closure: The incision is self-sealing and typically does not require sutures.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive care instructions and follow-up appointments.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Multifocal IOL Surgery: $2,500 – $5,500
- Multifocal IOL Implantation: $1,000 – $2,500
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $3,700 – $8,550
Combined Cataract and Glaucoma Surgery
Definition and Details
Combined cataract and glaucoma surgery is performed on patients who have both cataracts and glaucoma, a condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure that can lead to optic nerve damage.
This procedure allows for the simultaneous treatment of both conditions, minimizing the number of surgeries and recovery time for the patient.
The surgeon typically combines techniques from cataract surgery with glaucoma surgical methods, such as trabeculectomy or tube shunt placement.
This approach is beneficial for patients with moderate to advanced glaucoma who also need cataract surgery. It requires specialized skills and knowledge to ensure the success of both components of the procedure.
Procedure Steps
- Preoperative Evaluation: Comprehensive eye exam to assess cataract severity and glaucoma status.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is administered for patient comfort.
- Incision Creation: A small incision is made in the cornea.
- Capsulotomy: An opening is created in the lens capsule.
- Cataract Removal: The cloudy lens is removed using phacoemulsification.
- Glaucoma Surgery: The surgeon performs either a trabeculectomy or places a tube shunt to manage intraocular pressure.
- IOL Insertion: An intraocular lens is implanted to restore vision.
- Closure: The incisions are closed, often self-sealing.
- Postoperative Care: Patients receive instructions for postoperative care and follow-ups.
Cost Breakdown
- Preoperative Consultation: $100 – $300
- Combined Surgery: $3,000 – $6,000
- Monofocal IOL Implantation: $300 – $1,000
- Postoperative Follow-up Visits (2-3 visits): $100 – $250
- Total Estimated Cost: $3,500 – $7,550
The Importance of Choosing the Right Clinic
Selecting the appropriate clinic for cataract surgery in Turkey is paramount. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a facility:
- Accreditation: Ensure that the clinic is accredited by recognized organizations, ensuring quality and safety standards.
- Surgeon Credentials: Research the qualifications and experience of the ophthalmologists performing the surgery. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous patients.
- Technology and Equipment: Modern clinics should use state-of-the-art equipment and technology, enhancing surgical precision and outcomes.
- Patient Support Services: Look for facilities that offer comprehensive support services, including language assistance, transportation, and accommodation options.
How to prepare for a Cataract operation?
Personal Preparations
Educate Yourself About Cataract Surgery
- Research the Procedure: Start by immersing yourself in the details about cataracts and the surgical procedure. Understanding the causes and effects of cataracts helps demystify the surgery. Knowledge about the different types of intraocular lenses (IOLs) and their functionalities can help you make informed decisions about which option best suits your lifestyle.
- Understand Outcomes and Risks: It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the potential benefits, risks, and complications associated with cataract surgery. For example, while the surgery is highly successful in restoring vision, some risks may include infection, retinal detachment, or persistent visual disturbances. A realistic understanding of these aspects can help you manage your expectations effectively.
Organize Transportation and Support
- Arrange for a Companion: On the day of surgery, ensure that you have someone who can accompany you. Anesthesia, whether local or general, will impair your ability to drive. Having a trusted friend or family member by your side not only helps with logistics but also provides emotional support, which can be invaluable.
- Plan for Post-Surgery Care: Your companion’s role doesn’t end with transportation. Discuss their responsibilities in your post-surgical care, which might include assisting with daily tasks, preparing meals, and helping monitor your recovery. Knowing you have help will allow you to focus on healing.
Review Medications and Medical History
- Create a Medication List: Document all medications you take regularly, including dosages, frequency, and any supplements. This list is vital for your healthcare providers to understand your health context better and to avoid any potential drug interactions during your treatment.
- Disclose Medical Conditions: Be ready to discuss your complete medical history with your ophthalmologist. This includes any prior surgeries, chronic health issues (such as diabetes or hypertension), and allergies. Comprehensive knowledge of your medical background allows the surgical team to prepare for any complications that may arise.
Adjust Medications as Recommended
- Follow Medical Guidance: Your ophthalmologist may advise you to stop taking specific medications several days before surgery, particularly blood thinners or anti-inflammatory drugs. This is to minimize bleeding risks during the procedure.
- Consult on Herbal Supplements: Many patients may not consider herbal supplements as medications, but some can interfere with anesthesia or post-operative recovery. Be transparent with your doctor about all supplements you are taking.
Prepare for Post-Operative Recovery
- Gather Necessary Supplies: Before surgery, stock up on the essentials you will need during recovery. This includes prescribed eye drops to aid healing, protective sunglasses to shield your eyes from bright lights, and cold packs to reduce swelling. Having these items on hand will ensure you are prepared for your post-operative care.
- Create a Comfortable Recovery Area: Designate a space in your home where you can rest comfortably after the procedure. Make sure this area is free from bright lights and distractions, as sensitivity to light can increase after surgery.
Limit Certain Activities
- Avoid Strenuous Exercise: In the lead-up to your surgery, it’s crucial to refrain from high-impact activities or heavy lifting that could put undue stress on your body and eyes. Engaging in low-impact exercises, like walking, is typically acceptable unless otherwise directed by your physician.
- Reduce Screen Time: Limit your time spent on screens phones, computers, and televisions in the days before surgery. Prolonged screen time can lead to eye strain and fatigue, which can be counterproductive as you prepare for the procedure.
Follow Dietary Guidelines
- Dietary Adjustments: Adhere to any dietary recommendations provided by your doctor leading up to the surgery. This often includes maintaining hydration but limiting food and drink intake for a specific period before the operation.
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants, particularly those beneficial for eye health. Foods such as leafy greens, carrots, nuts, and fatty fish are known to support overall vision and can help prepare your body for surgery.
Manage Expectations and Prepare for Vision Changes
- Set Realistic Goals: While cataract surgery can significantly improve vision, it’s essential to understand that it may not restore perfect eyesight right away. Prepare for a period of adjustment as your eyes heal and adapt to their new lenses.
- Visual Aids: Discuss with your doctor the potential need for glasses or contact lenses after surgery, even if you opt for a multifocal lens. Understanding your long-term vision needs can help you make better plans for your recovery.
Protect Your Eyes
- Wear Sunglasses: Protect your eyes with high-quality sunglasses that block UV rays whenever you go outside, especially in the days leading up to surgery. This can help mitigate light sensitivity.
- Avoid Eye Makeup: In the week prior to surgery, abstain from using eye makeup, creams, or lotions around the eyes. This precaution reduces the risk of infection and irritation during the healing process.
Cultivate a Positive Mindset
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, or yoga. Reducing anxiety and fostering a positive mindset can enhance your overall surgical experience.
- Seek Emotional Support: Reach out to friends or family members for encouragement and support, or consider joining a support group for patients undergoing similar procedures. Connecting with others who have had similar experiences can provide valuable insights and comfort.
Professional Preparations with the Doctor
Schedule a Comprehensive Eye Exam
- Detailed Assessment: Prior to your surgery, you’ll undergo a comprehensive eye examination. This typically involves vision tests, measuring intraocular pressure, and a thorough assessment of the retina. The detailed exam helps your surgeon understand the severity of your cataracts and determine the most appropriate surgical approach.
- Identify Additional Issues: The examination can also uncover other eye conditions that may require treatment before or after cataract surgery. By addressing all ocular issues, your healthcare team can formulate a comprehensive treatment plan that ensures optimal results.
Discuss Anesthesia Options
- Understanding Anesthesia: Talk with your surgeon about the type of anesthesia that will be used during the procedure. Options may range from local anesthesia with sedation to general anesthesia, depending on individual needs and preferences. Each option has specific risks and benefits that your doctor will explain.
- Medical Clearance for Anesthesia: If you have any underlying health conditions, such as heart disease or respiratory issues, additional evaluations by a specialist (like a cardiologist) may be required to confirm that you are fit for the planned anesthesia.
Explore IOL Options with Your Surgeon
- Types of Intraocular Lenses: During your consultation, your surgeon will explain the different types of IOLs available such as monofocal, multifocal, toric, and accommodating lenses and their specific functionalities. Understanding these options is critical for making an informed decision that aligns with your vision needs and lifestyle.
- Personalized Lens Selection: Your doctor will provide recommendations based on detailed measurements of your eye, visual needs, and lifestyle considerations. This collaborative decision-making process ensures that you select the most suitable lens for your unique situation.
Review Preoperative Instructions
- Written Guidelines: Your surgeon will supply you with comprehensive preoperative instructions outlining everything from fasting requirements to medication adjustments. Thoroughly understanding these guidelines is essential for your safety and the success of the procedure.
- Clarify Questions: Before your surgery, take the time to clarify any questions you may have regarding the instructions. Understanding every detail will help you feel more prepared and confident going into the surgery.
Conduct Necessary Lab Tests
- Blood Tests: Depending on your medical history, your surgeon may request blood tests or other assessments to check for underlying health conditions that could impact the surgery or recovery.
- Comprehensive Health Evaluation: For patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, additional evaluations may be necessary to ensure that all health factors are adequately managed before surgery.
Maintain Open Communication with Your Surgeon
- Discuss Concerns and Questions: Establish a rapport with your surgeon, enabling you to communicate openly about any concerns or questions you may have. Transparency is crucial for addressing potential risks and ensuring that you feel secure in the decision to proceed with surgery.
- Clarify the Surgical Process: Request a detailed overview of what to expect during the surgical procedure, including the steps involved and how long the operation is likely to take. Knowing the process can alleviate anxiety.
Understand the Surgery Process Thoroughly
- Detailed Explanation of the Steps: Ensure that your surgeon explains each aspect of the surgical process. This includes what will happen during the surgery itself, what type of anesthesia will be used, and how long recovery may take.
- Emergency Protocols: Clarify the emergency protocols that the surgical team has in place should any unexpected complications arise during the procedure. Knowing this can help reassure you and build confidence in your healthcare providers.
Schedule Follow-Up Appointments
- Postoperative Care Plan: Your doctor will outline a schedule for follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and assess the healing process. These check-ins are vital for catching any potential complications early and ensuring your eye health remains stable.
- Discuss Vision Goals: During these follow-ups, take the opportunity to discuss your vision goals and any changes you may experience post-surgery. Adjustments may be necessary to optimize your visual outcomes.
What happens during a Cataract operation?
Anesthesia Administration
Step Overview: The first step in cataract surgery is the administration of anesthesia to ensure the patient remains comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure. Anesthesia can be localized, systemic, or a combination of both.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Preparation: The surgeon begins by discussing anesthesia options with the patient, assessing any medical conditions that may affect anesthesia choice. Patients may be given the option of sedation or simply local anesthesia.
- Local Anesthetic: Administers anesthetic eye drops to numb the eye and surrounding area. This typically involves a combination of proparacaine or tetracaine drops, which provide rapid numbing effects.
- Sedation: If intravenous sedation is used, the anesthesiologist or surgeon administers a sedative, carefully monitoring the patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The goal is to keep the patient relaxed without completely unconsciousness.
Patient Positioning and Eye Preparation
Step Overview: Proper positioning on the operating table is essential for both patient comfort and surgeon accessibility. The eye being treated is prepared meticulously to ensure a sterile environment.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Positioning: The patient is carefully laid flat on their back on the operating table, ensuring their head is stable. An adjustable headrest may be used to keep the head in place.
- Sterilization: The surgeon cleans the area around the eye using antiseptic solutions, such as povidone-iodine, to eliminate bacteria and minimize infection risk.
- Draping: A sterile drape is placed around the eye, covering the rest of the face and body to maintain a sterile field. This drape usually has an opening for the eye, allowing full access while preventing contamination.
Creating an Incision
Step Overview: The surgeon creates a small incision in the cornea, which serves as the entry point for the surgical instruments. This incision is typically made with a microkeratome or a femtosecond laser.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Precision Cutting: Utilizing a surgical knife, the surgeon carefully makes a self-sealing incision, typically measuring between 2.2 to 2.8 millimeters. This precise technique helps to minimize trauma to surrounding tissues.
- Ensuring Integrity: After the incision is made, the surgeon checks for any bleeding and ensures the incision is clean and free from debris before proceeding.
- Preparation for Further Steps: The incision is designed to facilitate subsequent steps without causing significant discomfort or complications during the surgery.
Capsulotomy
Step Overview: A capsulotomy involves creating an opening in the capsule that surrounds the lens of the eye. This step is crucial for accessing the cataract.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Creating the Opening: The surgeon uses a capsulorhexis forceps to carefully create a circular opening in the anterior capsule of the lens. This step is performed delicately to avoid damaging the surrounding tissue.
- Ensuring Adequate Size: The size of the capsulotomy is critical; it must be sufficiently large to allow for the removal of the cataract but not so large that it risks instability for the new lens.
- Manipulating the Capsule: If necessary, the surgeon gently lifts the capsule to facilitate better access and manipulation of the cataract.
Phacoemulsification of the Cataract
Step Overview: This is the key step in cataract surgery, where the cloudy lens is emulsified and aspirated from the eye using ultrasonic waves.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Introducing the Phaco Probe: The surgeon carefully inserts the phacoemulsification probe through the incision into the capsular bag where the cataract resides.
- Emulsifying the Lens: Utilizing ultrasound energy, the surgeon breaks the cataract into tiny fragments, which can then be easily removed. The power and frequency of the ultrasound waves are adjusted based on the density of the cataract.
- Aspiration: Simultaneously, the probe has a suction function that removes the emulsified lens material. The surgeon meticulously monitors the chamber to ensure all cataract material is completely aspirated, preventing any leftover debris that might affect vision.
IOL Insertion
Step Overview: Following the successful removal of the cataract, the surgeon inserts an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to replace the natural lens and restore vision.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Selection of IOL: Prior to surgery, the surgeon has predetermined the type of IOL based on individual patient needs. This decision is made based on measurements taken during preoperative assessments.
- Folding the Lens: The surgeon carefully folds the IOL to allow it to fit through the small incision. Advanced IOLs can correct for astigmatism and presbyopia, depending on the patient’s requirements.
- Positioning the IOL: Once inside the eye, the IOL is unfolded and positioned within the capsular bag. The surgeon takes great care to ensure it is perfectly centered and stable.
Stabilizing the IOL
Step Overview: After insertion, the surgeon checks to ensure that the IOL is stable and correctly positioned.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Alignment Check: The surgeon examines the IOL’s position relative to the pupil, ensuring that it is centered for optimal vision correction.
- Adjustments: If necessary, the surgeon may make slight adjustments to the lens position using specialized instruments to achieve the best alignment.
- Assessing Stability: The surgeon ensures the IOL is secure within the capsular bag and checks for any signs of potential complications that could arise from misalignment.
Fluid Exchange
Step Overview: After confirming the IOL is stable, the surgeon performs a fluid exchange to remove any residual viscoelastic substance used during the surgery and restore the eye’s natural pressure.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Washing Out Residual Materials: The surgeon carefully irrigates the eye with a balanced salt solution to flush out any remaining viscoelastic material or debris from the surgical area.
- Monitoring Intraocular Pressure: The surgeon measures the eye’s pressure, ensuring it returns to a normal range after fluid exchange.
- Checking Eye Shape: The surgeon observes the shape of the eye, ensuring that it remains stable and free from any irregularities following the procedure.
Closing the Incision
Step Overview: After all components are in place, the surgeon prepares to close the incision. Most cataract incisions are designed to be self-sealing, minimizing the need for sutures.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Inspecting the Incision: The surgeon examines the incision site for any signs of bleeding or leakage, ensuring it is secure and healing properly.
- Application of Antibiotics: A topical antibiotic solution may be applied to prevent infection, providing an additional layer of safety post-surgery.
- Sealing Techniques: In some cases, if the incision does not seal properly, the surgeon may use tissue adhesive or sutures to ensure the incision remains closed.
Final Examination and Recovery Preparation
Step Overview: The final step involves a thorough examination of the eye to confirm the success of the procedure before transferring the patient to the recovery area.
Doctor’s Actions:
- Postoperative Assessment: The surgeon evaluates the clarity of the vision and verifies that the IOL is positioned correctly, assessing for any complications.
- Instructions for Care: The surgeon provides detailed post-operative instructions, including guidelines for eye care, medications (such as anti-inflammatory and antibiotic eye drops), and activities to avoid in the early recovery period.
- Monitoring Transfer: The surgical team ensures that the patient is stable and comfortable before moving them to a recovery area for continued monitoring as they awaken from sedation.
Conclusion.
Cataract surgery in Turkey offers an effective solution for regaining clear vision at a fraction of the cost compared to many Western countries.
With a variety of procedures, types of lenses, and locations available, patients can make informed decisions that best suit their needs and budget.
When considering cataract surgery, it’s essential to take the time to research, understand the costs involved, and choose a reputable clinic and surgeon.
By investing in your vision today, you’re taking a significant step toward enhancing your quality of life.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to Turkish medical facilities to explore your options and schedule your consultation.

